Understanding LED Basics
- Forward Voltage (Vf): Each LED color has a specific forward voltage:
- Red LED: ~2.0V
- Green LED: ~3.0V
- Blue LED: ~3.0-3.2V
- White LED: ~3.0-3.4V
- Yellow/Orange LED: ~2.0-2.2V
- Forward Current (If): Most standard LEDs are rated for 20mA (0.02A).
Resistor Calculation Formula
To calculate the resistor value:
R = (Vsource - Vf) / If
- R: Resistor value in ohms (Ω)
- Vsource: Source voltage (12V in this case)
- Vf: LED forward voltage
- If: Desired LED current (usually 0.02A)
Resistor Values for Each Color LED
| LED Color | Forward Voltage (Vf) | Calculated Resistor (R) | Nearest Standard Resistor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 2.0V | 500Ω | 510Ω |
| Green | 3.0V | 450Ω | 470Ω |
| Blue | 3.2V | 440Ω | 470Ω |
| White | 3.4V | 430Ω | 470Ω |
| Yellow/Orange | 2.2V | 490Ω | 510Ω |
Choosing the Right Resistor
- Standard Values: Use the nearest standard resistor value equal to or slightly higher than the calculated value.
- Power Rating: Ensure the resistor can handle the power dissipation using the formula:
P = (Vsource - Vf)² / R. Typically, ¼-watt resistors are sufficient.
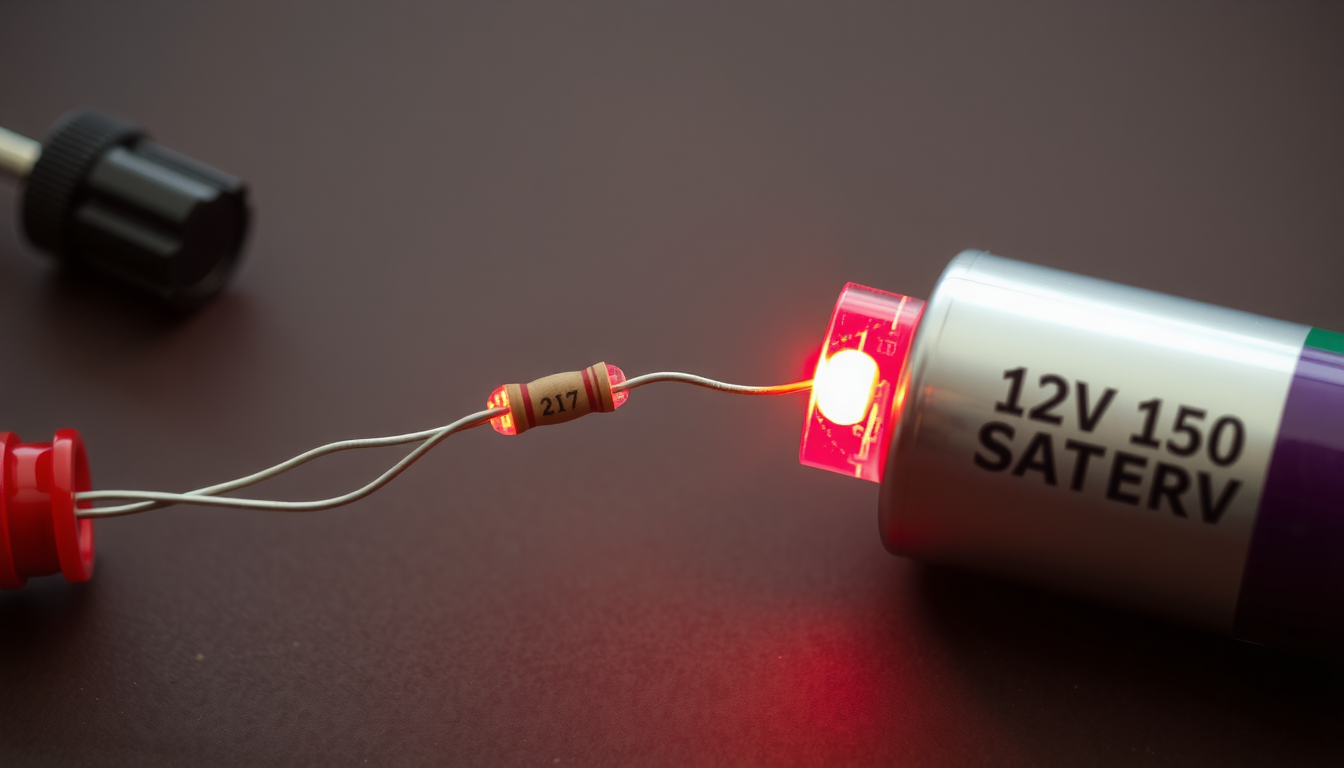
Practical Example
If you want to connect a red LED to a 12V battery:
- Calculate the resistor value:
R = 500Ω. - Select the nearest standard resistor: 510Ω.
- Wire the resistor in series with the LED and connect them to the 12V battery.
Using Multiple LEDs
- In Series: Add the forward voltages of all LEDs. The resistor value is calculated for the total forward voltage.
- In Parallel: Each LED needs its own resistor to ensure uniform current distribution.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct resistor ensures the longevity and optimal performance of your LEDs. By calculating the resistor value based on the LED's forward voltage and current, you can safely connect any color LED to a 12V battery.